IoT has become the latest buzzword, right up there with big data and predictive analytics. But what exactly is the internet of things? How does it work? What opportunities does it present?
These questions form the basis of this article. The Internet of Things means different things to different people, but basically, it describes the increasing presence of network-connected devices. These can be sensors embedded in objects or environments to gather data, or they can be your devices that connect to the internet to make your life more convenient.
What Is Internet of Things?
The IoT is a network of physical objects or “things” embedded with electronics and software that enable them to communicate and share data over the Internet.
The idea behind IoT is that everyday objects should be able to connect to the internet and share information. This allows consumers to use their smartphones or other devices to control their homes remotely.
How Does Internet of Things Work?
The Internet of Things (IoT) works in such a way that as digital infrastructure, it interconnects physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other items—anything that has an “Internet address” and can send and receive data.
IoT allows more interactive communication between these devices. As more objects are connected to the Internet, they become part of IoT.
This is made possible by enabling objects to be sensed or controlled remotely across existing network infrastructure, creating opportunities for more direct integration of the physical world into computer-based systems, resulting in efficiency improvements, economic benefits, and reduced human intervention.
When IoT is augmented with sensors and actuators, the technology becomes an instance of the more cyber-physical systems, which also encompasses technologies such as smart grids, smart homes, intelligent transportation, and smart cities. Each thing is uniquely identifiable through its embedded computing system but can interoperate within the existing Internet infrastructure.
This information society will be built on top of an “information-based society” that has developed over decades based on computers and telecommunications networks that transmit information quickly and easily around the world.
As part of this process, the IoT will connect people, processes, data, and things using intelligent networks capable of collecting data from sensors or other sources at any place on Earth or in space.
Each object has a unique identifier (UID) which can be used by other devices or systems to identify it on the network without having physical access or line-of-sight visibility. This allows the devices to be remotely monitored and/or controlled over long distances without needing human intervention.
Diagram: How IoT Works
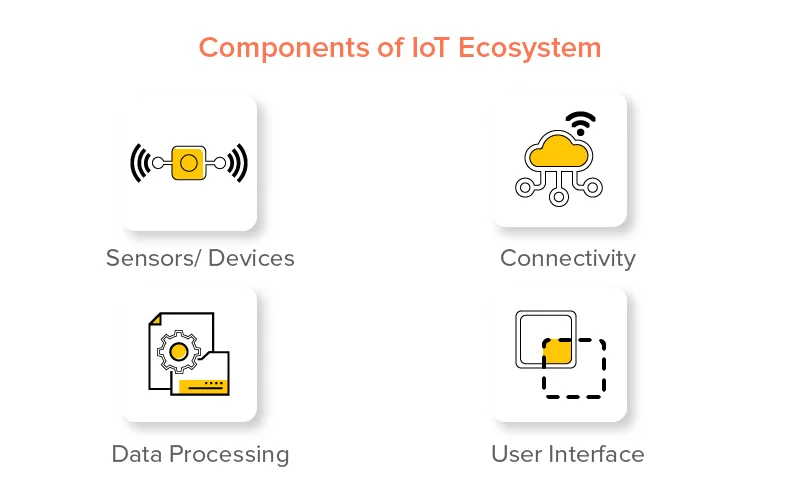
A complete IoT system integrates four distinct components:
1. Sensors
A sensor or device is any object that can detect and measure a condition or event. They can be embedded in almost anything — from buildings to cars to industrial equipment.
They are equipped with specialized software and hardware systems to perform particular functions at specific times — for example, when a door opens or closes or when someone walks through it.
Sensors can also be used to track movements within a building or facility, such as identifying when people enter or exit specific spaces to improve security or reduce energy usage by automatically turning off lights when they’re not needed anymore.
2. Connectivity
The connectivity of the Internet of Things is arguably its most vital attribute. Without it, there wouldn’t be much value in the set of devices that fall under the Internet of Things umbrella.
To define it, the connectivity of the Internet of Things is its ability to connect to another device or computer wirelessly or through wires.
Connecting devices to each other and the Internet allows them to share information in real-time. This can happen in many ways, including via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or connecting directly to the internet via ethernet.
3. Data Collection & Processing
Data collection refers to the process of gathering data from various sources and putting it into one place for analysis.
Several types of data can be collected, including sensor readings (temperature, humidity), location information (GPS coordinates), and audio recordings.
Also, processing of data received from sensors or other sources into insights that can be analyzed by people. It’s done through cloud-based platforms or other technologies that can process data faster than humans alone can.
Data processing is used in analytics, machine learning, AI/cognitive computing, predictive analysis, and many other applications.
4. User Interface
The user interface is the primary means of interaction between a human and the Internet of Things. It is used to provide information to the user, as well as to receive input from them.
For example, if you want to turn on your lights, you would use the user interface to do so by pressing a button on the wall or using your smartphone. It can also be as complex as a touch screen with a full-color display and graphics.
What Are The Advantages of IoT?
IoT is not just about connecting devices to the Internet. It’s about connecting things and people in a way that creates new possibilities. Here are some of the advantages of IoT:
Cost savings: IoT reduces costs by eliminating manual processes, increasing efficiency, improving output quality, and reducing waste. For example, connected sensors can be used to monitor utility usage and reduce energy costs by switching off power to non-essential areas during peak demand periods.
Safety: Connected sensors can help prevent accidents by alerting users or authorities about unsafe situations before they occur. For example, you could set up an alarm system that automatically alerts fire departments if your home catches fire.
Convenience: Connected devices allow us to access information and services remotely through mobile apps or web browsers — no matter where we are or what device we’re using (e.g., laptop, mobile phone). This makes it easier for people to do their jobs while away from the office and enjoy more free time with family members who live elsewhere.
Efficiency: IoT technology can automate jobs that would otherwise require human labor. This could mean increased productivity for employees who don’t need to waste time on tedious tasks like checking inventory or cleaning up after customers leave the store.
Increased customer engagement: Consumers can use smart apps like Amazon Alexa to shop online or check on their home security system from anywhere in the world at any time of day.
Better decision making: IoT data collection allows businesses to make better decisions about product development and marketing strategies based on real-time feedback from customers who have tried their products or services in different ways than expected.
Applications of Internet of Things
Smart Grid
The Internet of Things is a great way to monitor the energy consumption of your home or business. You can use it to check on your energy usage and see how much each appliance costs you on a daily, weekly, and monthly basis.
This can help you cut down on your electricity bills by making sure that you turn off appliances when they’re not in use, or by using a smart power strip that will automatically cut power to electronics when they’re not in use.
If you have solar panels, adding an Internet-connected power management system allows you to monitor their output and make sure they’re working properly.
Smart Home Security System
The Internet of Things also makes it possible for homes and businesses to have smart security systems that are controlled remotely through their smartphones or computers.
These systems allow users to arm and disarm their alarms from anywhere in the world, as well as receive notifications if there’s an intruder inside their home or office building.
Many alarm systems are designed so that they can be integrated with other smart devices in the home, allowing users to turn lights on and off remotely and control other devices from one central hub without having to leave their computer chair or smartphone screen.
Smart Cities
Smart cities use sensors in public spaces (i.e., traffic lights) to monitor traffic conditions so that authorities can make better decisions regarding traffic flow management and public transport schedules with minimal human intervention required.
Furthermore, smart city services may also include smart parking solutions which help drivers find parking spots.
Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, the Internet of Things is being used to improve patient care and reduce costs. The IoT is helping hospitals monitor patients more closely, so they can be alerted to any sudden changes in their condition.
This information can then be used by doctors and nurses to provide better care for patients.
For example, heart monitors can alert doctors if a patient’s heart rate increases suddenly or decreases significantly. This can help prevent serious health issues like heart attacks and strokes.
Agriculture
The Internet of Things is already being used to improve agriculture in many ways. From monitoring soil conditions and crop growth to gathering data on livestock, farmers are using the data to make more informed decisions about how to farm their land.
Farmers can also use the data collected by IoT devices to better plan for future harvests.
Logistics & Transportation
Improving the efficiency of logistics and transportation has been one of the biggest drivers behind the growth of IoT over the past several years. The ability to track goods in real-time has made it easier for companies to manage inventories, reduce costs and improve supply chains.
This will continue to be an important application as more companies embrace connected technologies like autonomous vehicles, smart sensors, and other monitoring systems to improve their services.
Industrial Manufacturing
The industrial manufacturing sector is another area that’s seeing significant growth from IoT applications like smart factory technology, which allows manufacturers to monitor production lines from a central location using data collected from sensors installed throughout their facilities.
This helps them ensure that each step in the production process runs smoothly so they can produce products with less waste and at a lower cost than ever before — with fewer human errors along the way as well.
Water Supply
In the world of IoT, water supply is a great example of how we can use technology to improve our lives. In cities like New York City, there are sensors in the water pipes that can detect leaks and send alerts when there’s a problem.
We can also use sensors to monitor water quality throughout the system and make sure that it’s safe for consumption.
This will enable cities to reduce their water usage by ensuring that residents aren’t using excess amounts of water when they don’t need to, for example, during rainstorms.
Conclusion
In the next few years, you will see more and more devices hooked up to the internet. Whether it be your oven or your refrigerator, or even things that we have not thought of yet—everything is becoming ‘smart’.
Technology like IoT opens up a whole new range of possibilities for us to explore. In turn, this will empower people in ways we never imagined before. This could be the new way in which technology helps us change the world around us.
FAQs
How does IoT work in simple terms?
IoT works by connecting various devices to the internet. These devices can be anything from a Smartphone to a laptop or even your home appliances. The collected data is stored in any number of databases around the world and then interpreted using the software.
Is a smartphone an IoT device?
Yes, a smartphone is an IoT device. It communicates with a server and sensors to gather data about the user. Then, it uses that data to control other devices and things around it.
What is the difference between IoT and AI?
AI and IoT represent two of the biggest technologies that are part of the tech revolution. While both involve learning, computing, and communication; the primary difference is in their usage. AI uses learning to improve its decision-making ability, while IoT uses learning to improve its communication abilities.
What is the goal of IoT?
The goal of IoT is to create a smart, connected world. With the everyday devices, we use becoming smarter and helping us live better lives, the Internet of Things has the potential to profoundly change our world for the better.
If you liked this article, then please subscribe to our YouTube Channel for WordPress video tutorials. You can also find us on Twitter and Facebook










